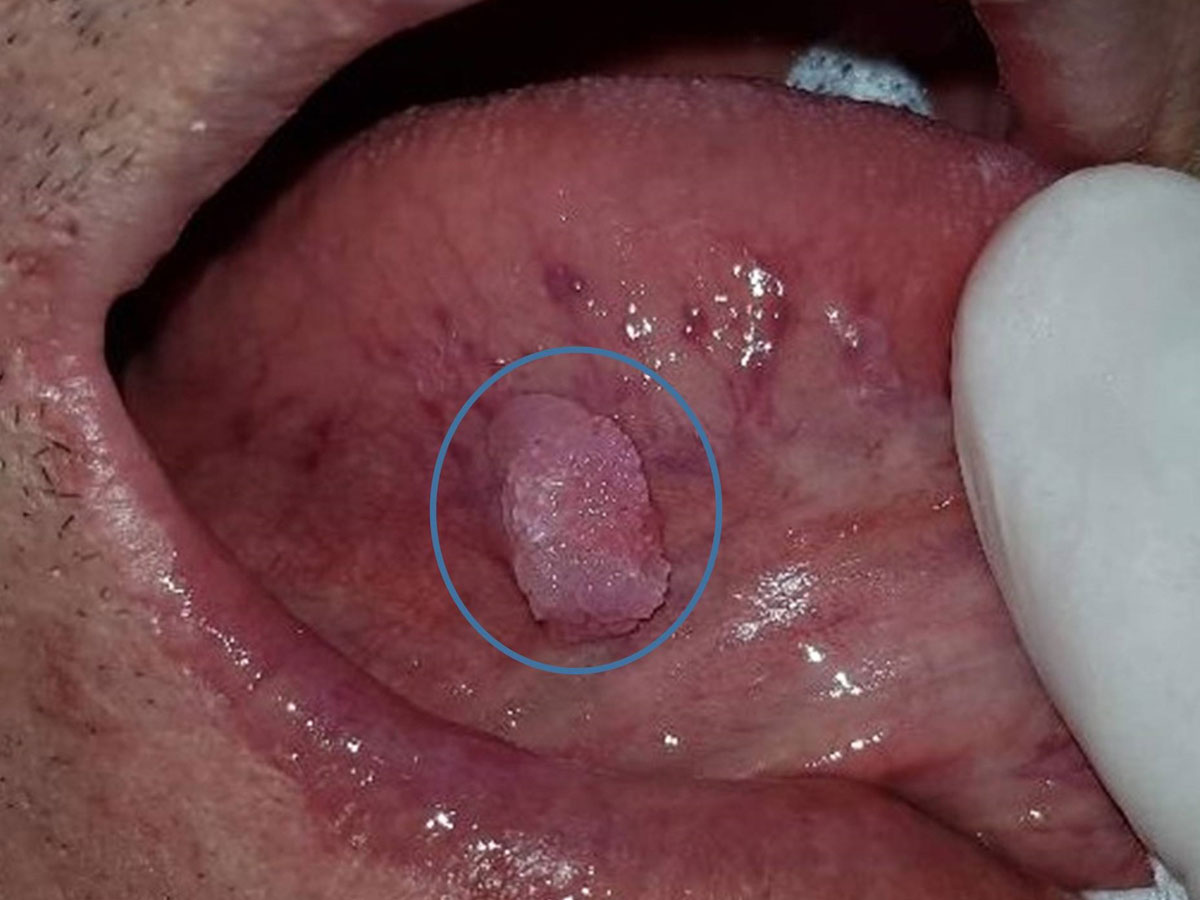
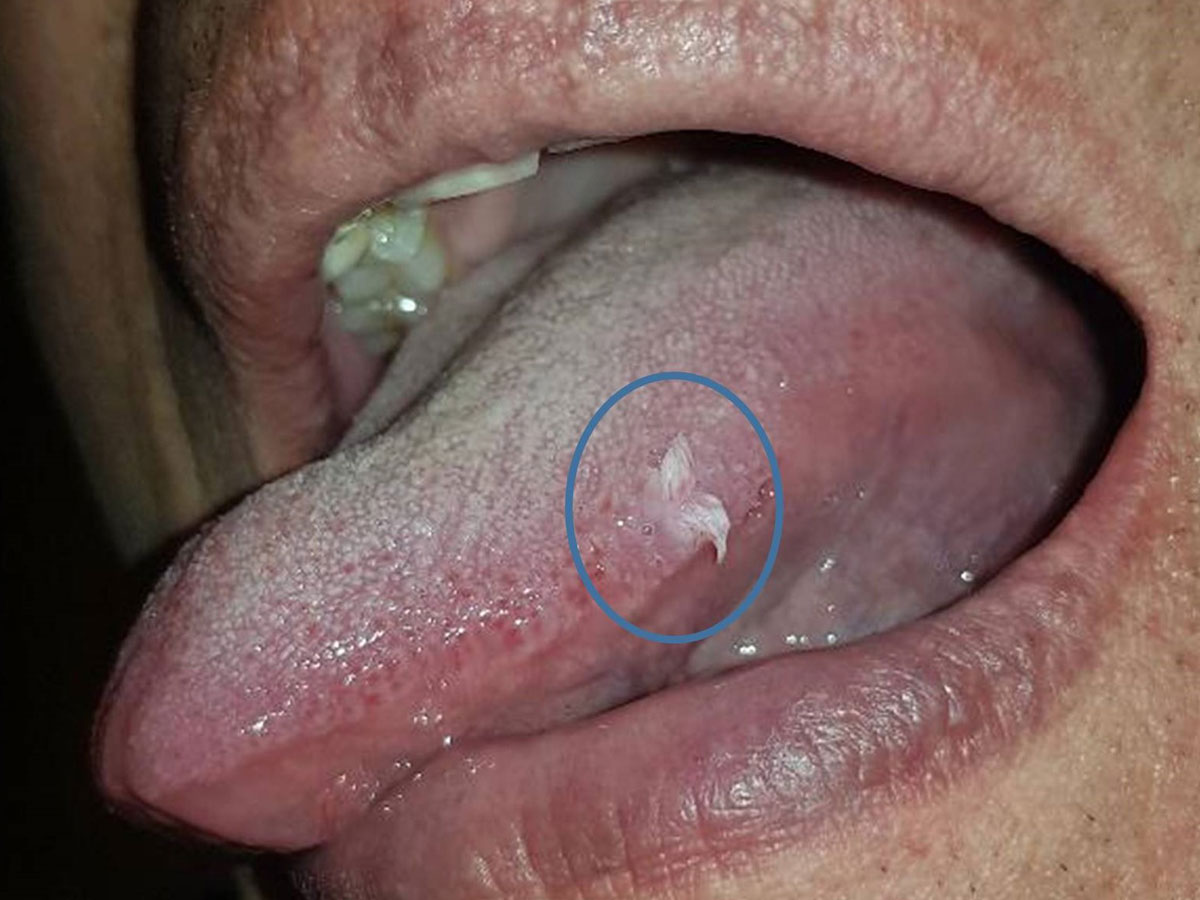
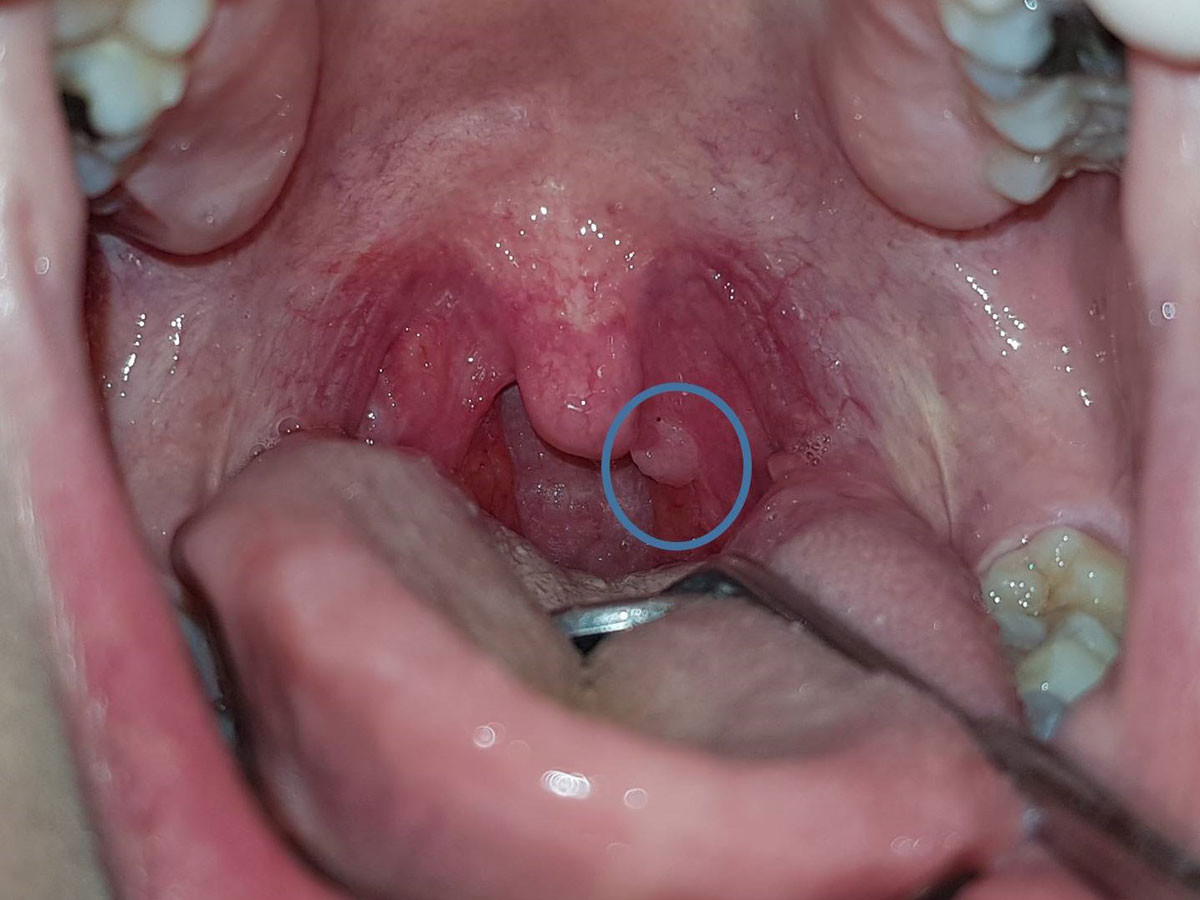
A variety of strains of the virus are also thought to be responsible for a number of benign lesions of the mouth such as papilloma, common warts, condyloma acuminatum and focal epithelial hyperplasia, as well as HPV + oropharyngeal cancer. In recent years, oncogenic strains of HPV have been documented to be causally associated with cancers that develop at the base of the tongue, tonsils and pharynx, making HPV infection an independent risk factor for this type of cancer.
Evidence suggests that oral HPV is mainly transmitted through oral sex, with the risk of infection increasing depending upon the number of sexual partners. Smoking and alcohol also appear to be associated with an increased risk of such lesions.
HPV lesions are asymptomatic and are usually discovered by chance during oral examination by the patient or dentist. However, over time, these lesions may become noticeable to the patient due to an increase in size. In general, these tumors, single or confluent, have an exophytic papillary surface and a cauliflower-like appearance. In the case of oropharyngeal cancer, due to the location of the lesion in the posterior part of the mouth, the patient will hardly notice the lesion visually, however he may complain of difficulty in swallowing, possible swelling of the tonsils or cervical lymph nodes, a sore throat, hoarseness and a persistent cough.
Regarding treatment, benign lesions are treated with standard surgical scalpel surgery. It is advisable to follow-up with the patient regularly for some time in order to exclude the possibility of a lesion that was initially indistinguishable due to its infinitesimal size as well as the exclusion of possible re-infection by the partner.