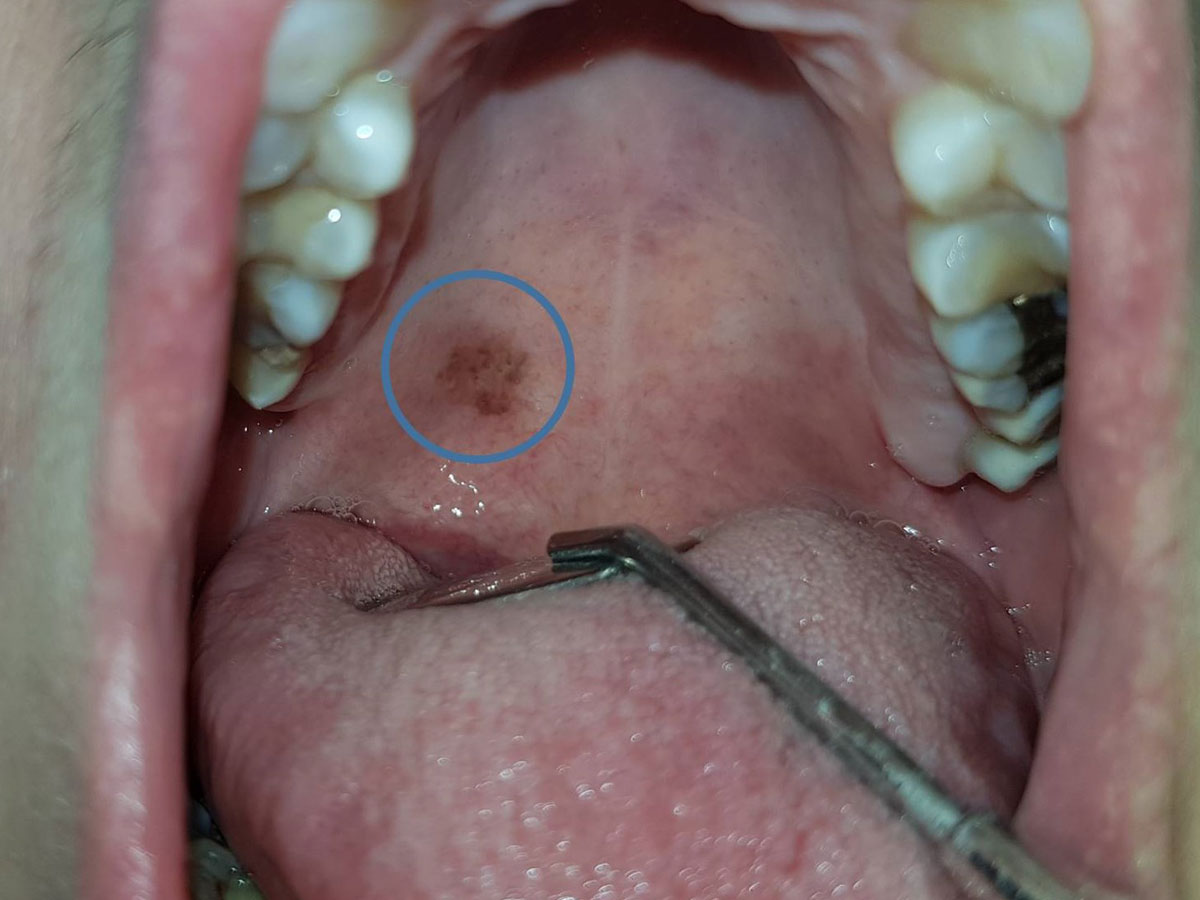
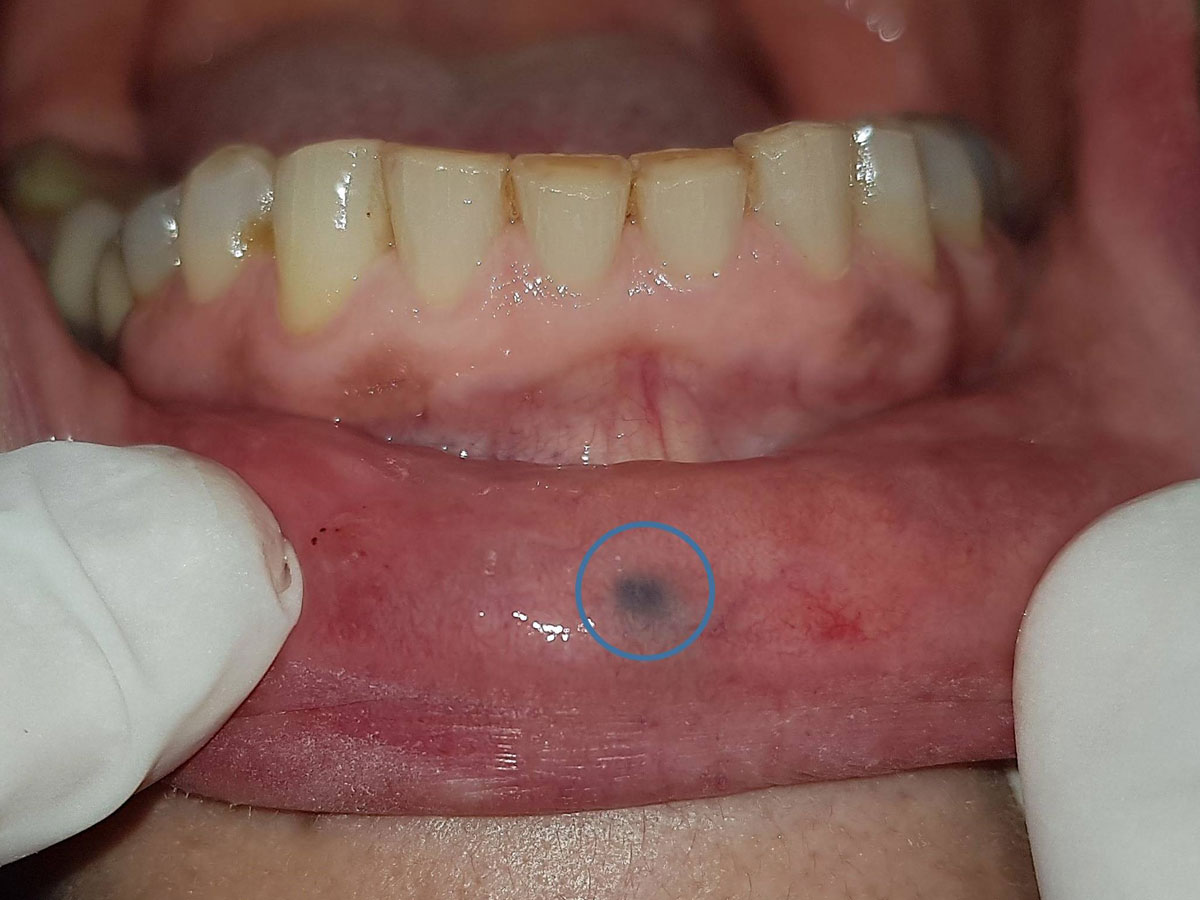
Regarding the origin of such spots, there can be a wide range of causes. Their evaluation requires taking a history of the patient with scrutiny, a thorough clinical examination accompanied by a biopsy and a histopathology examination, except in cases where the clinical signs and medical history almost certainly indicate the innocent nature of the lesion.
The detailed description of the pigmented lesions goes beyond the scope of this brief summary. In general, the exact color, location, distribution, duration, changes in size, color or peripheral boundaries, drug use, and family history are all important elements that will contribute towards an accurate diagnosis.
Spots of this type can often be considered normal, in the context of racial pigmentation while other common causes include smokers’ melanosis and discolorations attributed to common dental materials such as amalgam and silver cones. Among other causes, a relatively large class of drugs taken on a long term basis may be related to the development of brown spots in the mouth as well as neoplasms in the form of nevi and less often melanoma. Finally, there are systemic pathological conditions and syndromes as well as vascular lesions that the Oral Medicine specialist must keep in mind when investigating discolored spots in the mouth.