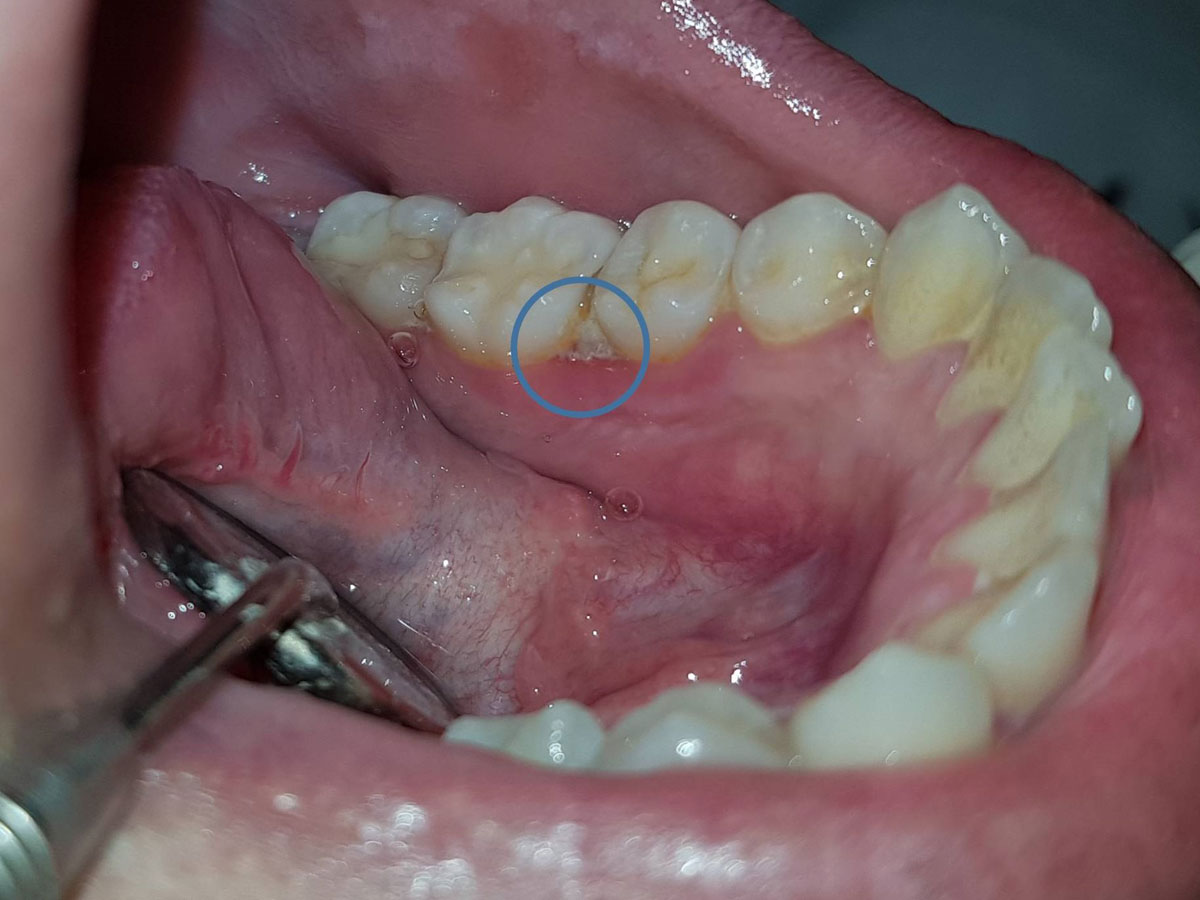
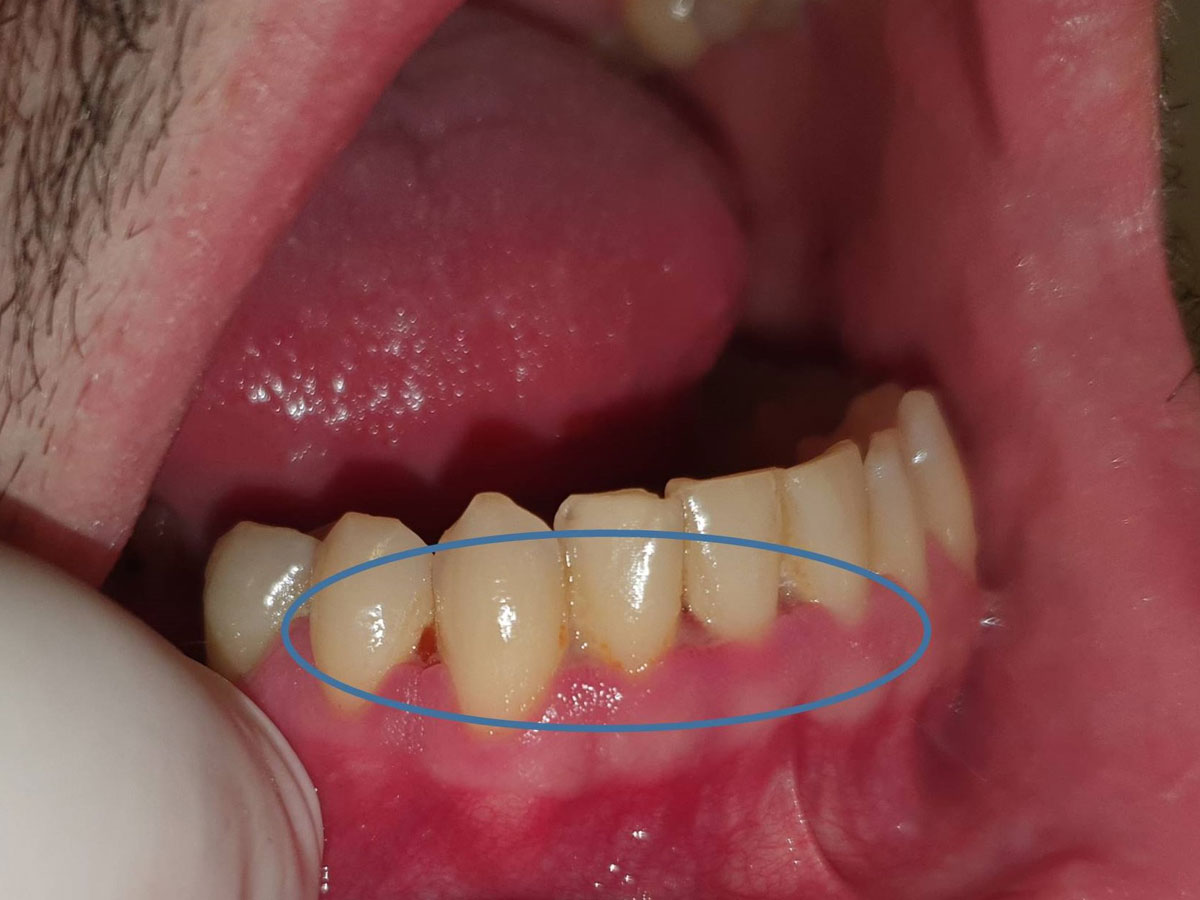
Predisposing factors that may cause the disease include conditions presenting themselves locally or systematically, in particular conditions of intense stress, poor diet, immune deficiencies, poor oral hygiene and smoking.
Regarding diagnosis, a detailed history of the patient’s health and a thorough clinical examination is required. It is an acute condition with severely painful symptoms. The patient may experience general malaise, fever, cervical lymphadenitis, halitosis, a distortion of the sense of taste, while in the gums intense redness, swelling, spontaneous bleeding and necrosis may appear, with ulcers originating from the interdental papilla and extending to the rest of the oral mucosa. If the disease is left without medical intervention, it can spread further, presenting as ulcerative periodontitis or stomatitis, respectively.
As far as medical treatment is concerned, the removal of any necrotizing tissues and administration of antibiotics with appropriate antimicrobial spectrum are required as well as oral solutions that release oxygen, disrupting the growth conditions of anaerobic microorganisms. Additionally, analgesics, good oral hygiene, periodontal treatment, laser therapy to the gums and adequate hydration and nutrition of the patient are recommended.