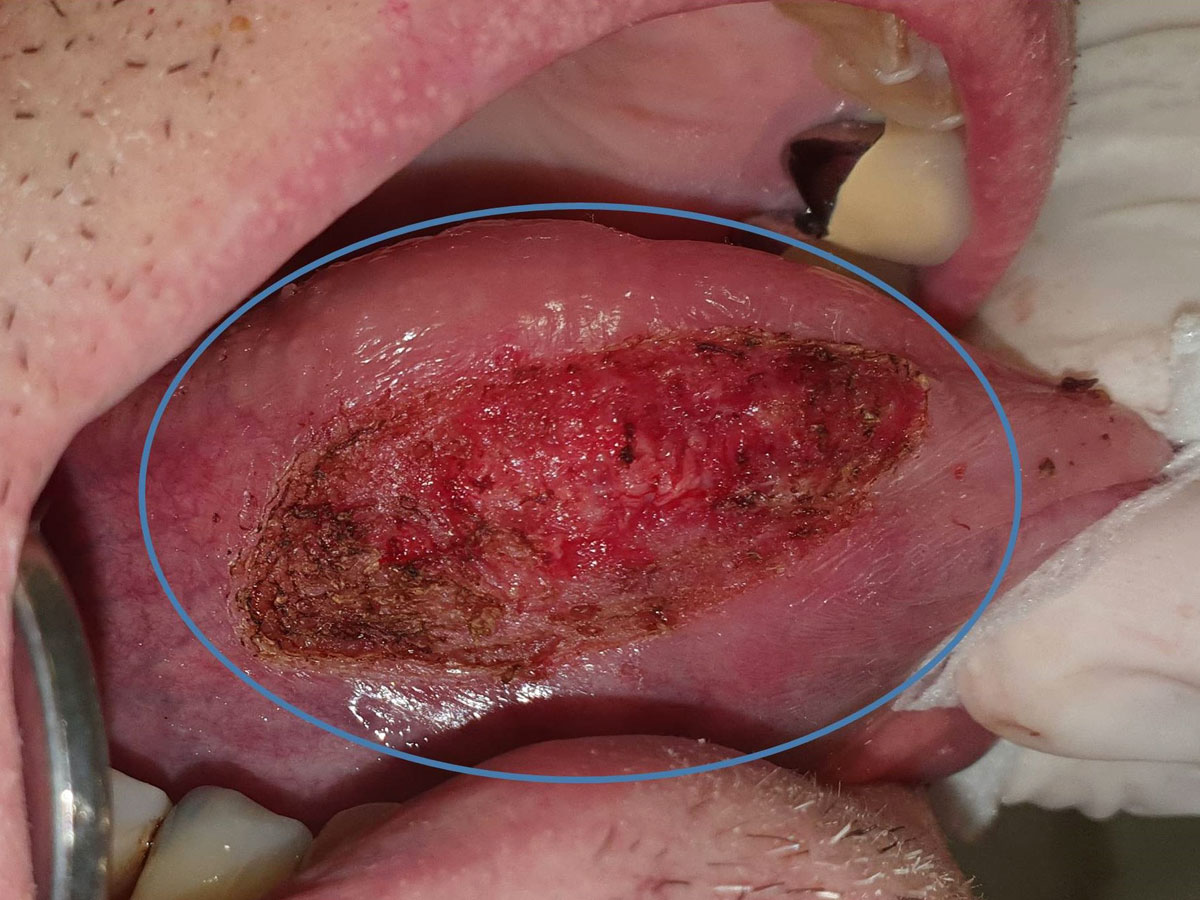
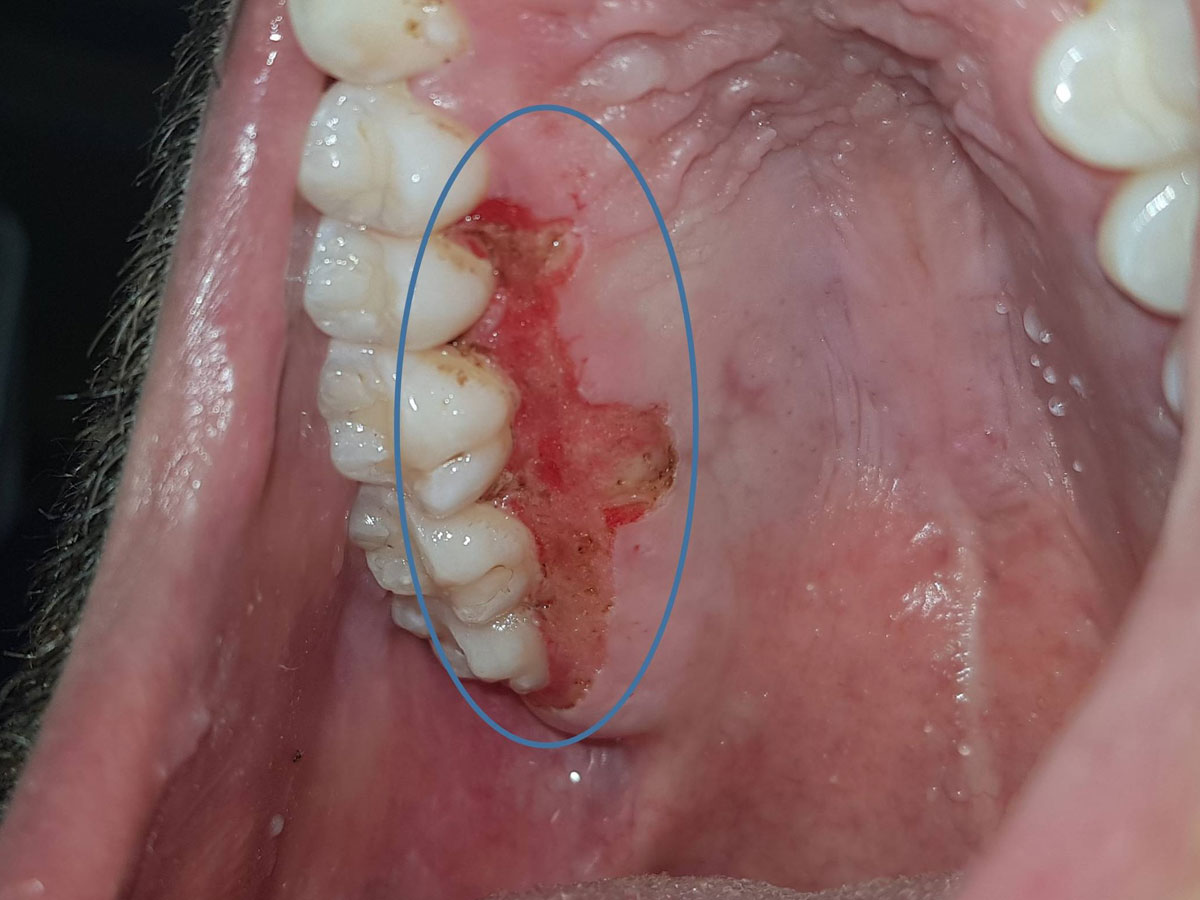
Among their main advantages is the hemostatic action, contributing to the successful execution of complicated and lengthy operations, which are performed without bleeding. This is in contrast to the use of a scalpel which would lead to a relatively bloody environment or would limit the area of the operation. Consequently, when using laser, a clear optical field is maintained, ensuring the high quality and successful execution of the surgical procedure, without the need for hasty and relatively careless manipulations due to a possible bleeding. Following such a procedure, the development of the hematoma is very limited to non-existent, while the need to modify the use of any medication that may affect the blood coagulation becomes less urgent. An additional reason that laser treatment contributes to the increased quality of an operation is the presence of a pointer on the edge of the laser beam that facilitates the manipulation of the medical practitioner. The above reasons lead us to favor the use of the laser to perform relatively extensive operations, or if there is concern regarding the bleeding that may occur, for example in the removal of extensive areas of leukoplakia.
In addition to the hemostatic action, their bactericidal property is important, which we use in cases of sterilization, including the treatment of simple or special types of gingivitis as well as in cases where the reduction of the microbial load of a wound is required, especially in high-risk patients, e.g. diabetics or patients with valvular heart disease.
A major area of intensive research is low-level laser therapy that offers significant benefits in cases of mucositis of oncology patients, as well as in operations for the removal of impacted teeth, bone regeneration and autoimmune diseases. This method reduces postoperative pain and swelling and contributes to tissue stimulation, it possesses anti-inflammatory properties and modifies mechanisms of the immune system.